Business Process Automation: Stop Working IN Your Business, Start Working ON It
Every successful entrepreneur reaches a critical inflection point where they realize they've become the bottleneck in their own business growth. They're working harder than ever, involved in every decision, and personally handling tasks that should be systematized. Business process automation offers a path out of this trap, enabling business owners to scale their operations without proportionally scaling their personal time investment.
The Entrepreneur's Dilemma
Business owners often pride themselves on knowing every aspect of their operations. This hands-on approach works well in the early stages when personal attention and quick decision-making drive initial success. However, this same approach becomes a limitation as businesses grow and complexity increases.
The symptoms of this challenge are familiar to most entrepreneurs. Email inboxes overflow with routine decisions that should be handled systematically. Time gets consumed by repetitive tasks that add little strategic value. Growth opportunities are missed because attention is focused on operational details rather than market expansion and competitive positioning.
Without systematic business processes, knowledge remains trapped in individual team members' heads rather than being captured in repeatable systems. This creates vulnerability when key people are unavailable and limits the business's ability to scale efficiently.
The transition from working in the business to working on the business requires deliberate effort to identify, document, and automate the processes that consume valuable time without requiring strategic oversight.
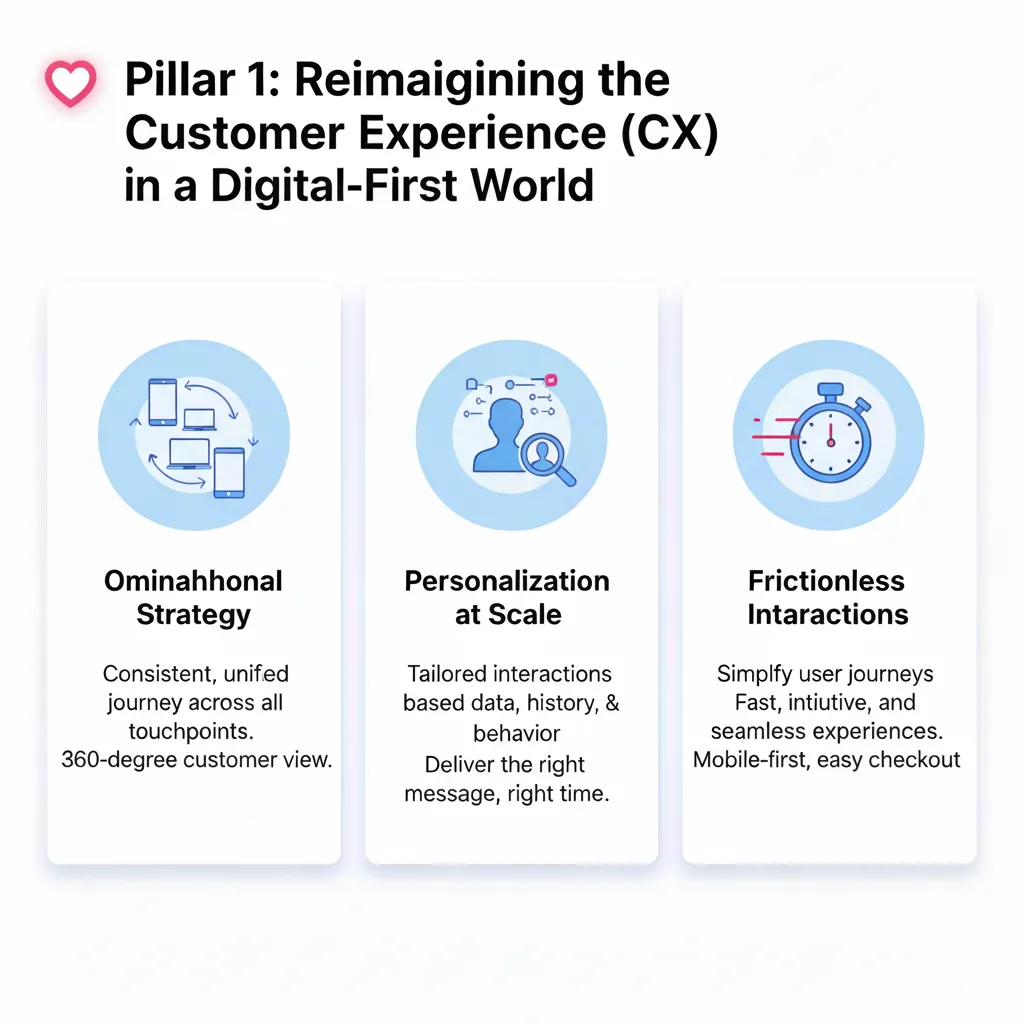
Identifying Automation Opportunities
Repetitive Task Analysis reveals the highest-impact automation opportunities in most businesses. Track how you and your team spend time for a typical week, categorizing activities by frequency, complexity, and strategic value. Tasks that are performed frequently, follow predictable patterns, and require minimal creative judgment represent ideal automation candidates.
Customer communication workflows often contain significant automation potential. Order confirmations, appointment reminders, follow-up sequences, and support ticket routing can be handled systematically without sacrificing quality or personalization.
Administrative processes like invoice generation, expense approvals, inventory updates, and reporting can consume enormous amounts of time when handled manually. These processes typically follow clear rules and criteria that translate well to automated workflows.
Decision Tree Mapping helps identify which business decisions can be automated based on predetermined criteria. If customer service responses follow predictable patterns based on inquiry type, these responses can be automated. If pricing decisions follow established rules based on order size or customer type, these calculations can be systematized.
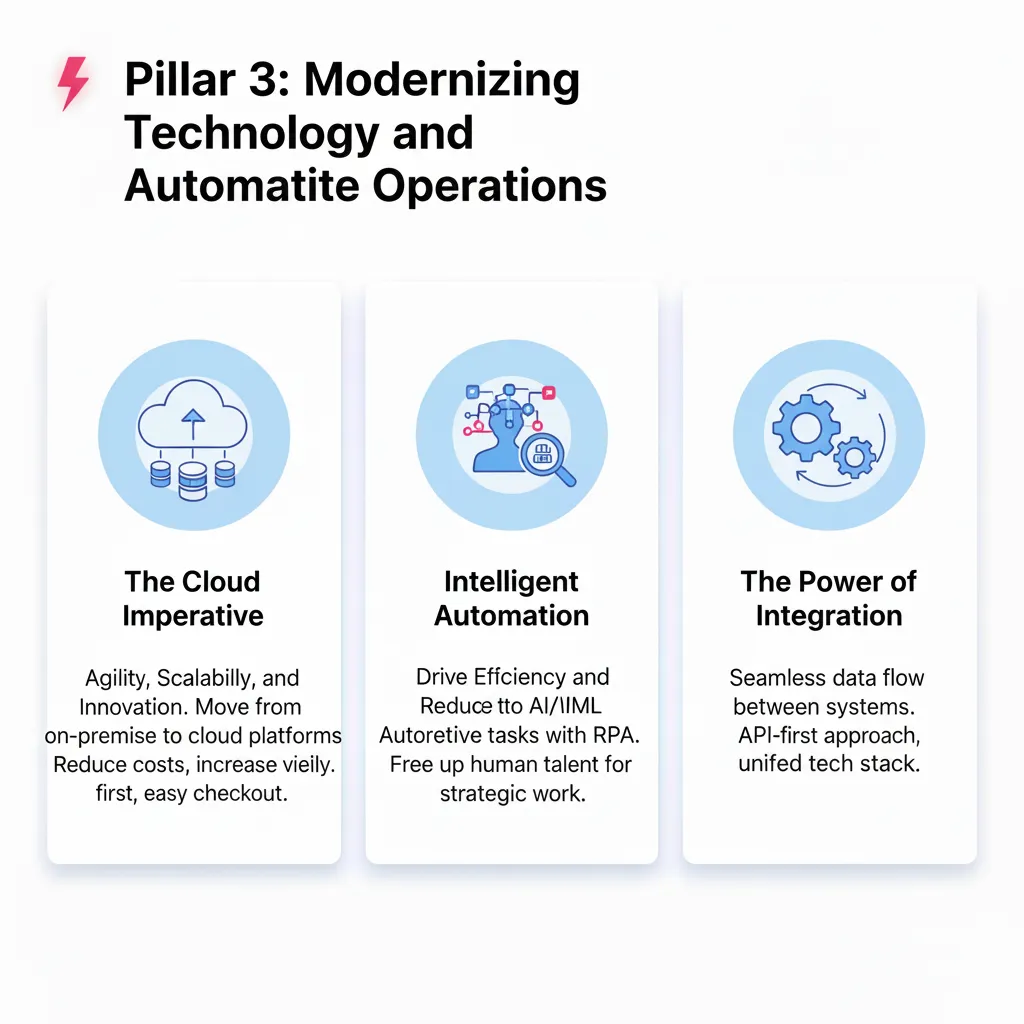
Technology Platform Selection
Modern automation platforms provide sophisticated capabilities that were previously available only to large enterprises with dedicated IT departments. Cloud-based automation tools offer small and medium businesses access to powerful workflow automation, data integration, and process management capabilities.
Integration capability represents the most critical factor in platform selection. Your automation platform should connect seamlessly with your existing CRM, email system, accounting software, and other business applications. Disconnected automation creates new inefficiencies rather than solving existing problems.
User-friendly interfaces ensure that business owners and team members can create and modify automated workflows without requiring technical expertise. Look for platforms that use visual workflow builders and plain-language rule definitions rather than complex programming languages.
Scalability considerations ensure your automation platform can grow with your business rather than requiring expensive migrations as your needs evolve. Choose platforms that offer advanced features you can grow into rather than basic tools you'll quickly outgrow.
Implementation Framework
Phase One: Foundation Building focuses on automating the most time-consuming, straightforward processes first. Email workflows, appointment scheduling, and basic customer communication sequences provide quick wins that demonstrate automation value while building team confidence in the new approaches.
Document existing processes before automating them to ensure you're systematizing effective workflows rather than inefficient practices. This documentation phase often reveals improvement opportunities that should be addressed before automation implementation.
Phase Two: Integration Expansion connects different business systems to create seamless information flow. When a customer places an order, the automated system might update inventory, generate invoices, schedule delivery, and trigger follow-up communications without requiring manual intervention at any step.
Data standardization becomes crucial as automation expands across different systems. Establish consistent formatting, naming conventions, and data entry practices to ensure automated workflows can process information reliably.
Phase Three: Intelligence Addition incorporates conditional logic and decision-making capabilities into automated workflows. Advanced automation can route support tickets based on complexity, adjust pricing based on customer history, or escalate issues based on severity criteria.
Measuring Automation Impact
Time savings represent the most obvious benefit of business process automation, but the impact extends far beyond simple efficiency gains. Track metrics like process completion time, error rates, customer satisfaction scores, and team member availability for strategic activities.
Cost analysis should include both direct savings from reduced manual effort and indirect benefits from improved consistency, faster response times, and enhanced customer experiences. Automation often improves service quality while reducing costs, creating compound value that justifies implementation investments.
Revenue Impact emerges as businesses can handle larger volumes of customers and transactions without proportional increases in overhead costs. Automated lead nurturing systems can manage hundreds of prospects simultaneously while maintaining personalized communication that would be impossible to achieve manually.
Team satisfaction typically improves as automation eliminates repetitive, low-value tasks that consume time without providing fulfillment. Team members can focus on creative problem-solving, strategic planning, and customer relationship building that utilize their skills more effectively.
Common Implementation Pitfalls
Over-automation represents one of the most common mistakes in process automation implementation. Not every business process should be automated, particularly those requiring human judgment, creativity, or complex problem-solving. Maintain human oversight for processes involving customer relationship management, strategic decision-making, and exception handling.
Insufficient testing can create problems that are more disruptive than the manual processes they replace. Thoroughly test automated workflows with sample data before deploying them in production environments. Establish monitoring procedures to detect and address issues quickly when they occur.
Change management challenges arise when team members resist new automated processes or continue using manual workarounds. Provide comprehensive training and clearly communicate the benefits of automation to encourage adoption and compliance.
Advanced Automation Strategies
Multi-trigger workflows create sophisticated automation that responds to combinations of events and conditions. A customer who hasn't made a purchase in 90 days and has low email engagement might trigger a different re-engagement sequence than a customer who hasn't purchased but actively engages with content.
Predictive automation uses historical data and pattern recognition to anticipate needs and trigger proactive actions. Inventory management systems can automatically reorder products based on seasonal patterns and current stock levels. Customer service systems can identify potential issues before customers report problems.
Cross-Platform Integration creates seamless workflows that span multiple business applications. A comprehensive automation platform might integrate CRM, email marketing, accounting, inventory management, and customer service systems to create unified business processes that operate efficiently without manual intervention.
Business process automation transforms operational efficiency while freeing entrepreneurs to focus on strategic growth activities. The businesses that implement automation systematically and thoughtfully create sustainable competitive advantages through superior operational efficiency, enhanced customer experiences, and improved scalability that enables confident expansion into new markets and opportunities.