From Startup to Scale-Up: How CRM Grows With Your Business
Business growth presents a series of operational challenges that can either accelerate success or create bottlenecks that limit expansion. Customer relationship management needs evolve dramatically as businesses progress from startup to scale-up, and the CRM systems that support early-stage operations often become inadequate as complexity increases. Understanding how to select and implement CRM technology that scales with growth prevents costly migrations and ensures operational continuity during critical expansion phases.
The Startup Phase: Foundation Building
Early-stage businesses often operate with minimal formal processes, relying on personal relationships and founder involvement to manage customer interactions. While this approach works when customer counts are low and complexity is minimal, it creates vulnerabilities that become problematic as growth accelerates.
Startup CRM needs focus on establishing basic systems that capture customer information, track interactions, and prevent opportunities from falling through the cracks. The emphasis should be on simplicity and rapid implementation rather than comprehensive feature sets that might overwhelm small teams.
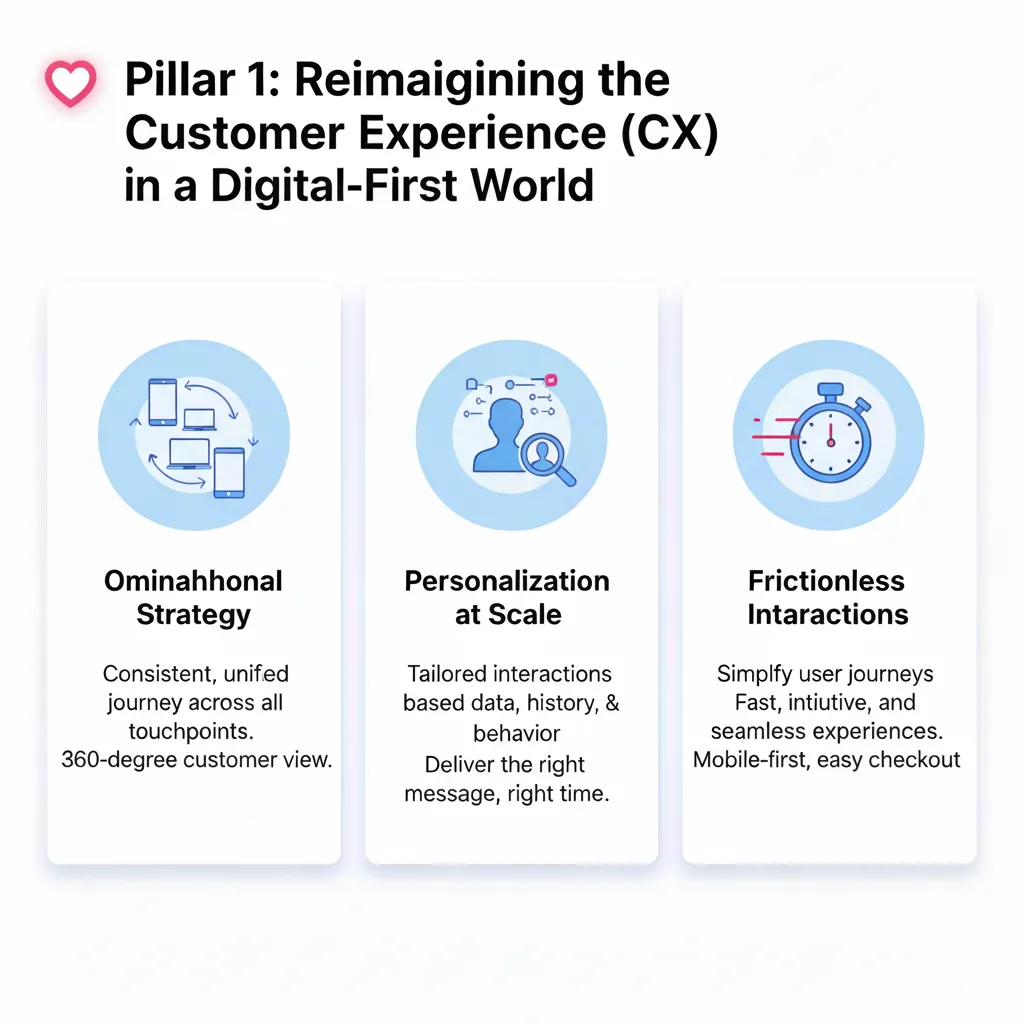
Essential Startup CRM Capabilities include contact management, basic sales pipeline tracking, and integration with email and calendar systems. These foundational features ensure customer information is centralized and accessible while supporting the informal, relationship-driven sales approaches that characterize early-stage businesses.
Data capture processes should be designed for simplicity and consistency from the beginning. Even simple contact forms and basic lead tracking create valuable historical data that becomes increasingly important as the business grows and customer patterns emerge.
Scalability considerations become crucial even at the startup stage. The CRM platform should offer advanced features that can be activated as the business grows rather than requiring complete system replacement when needs evolve.
Growth Stage Challenges and Solutions
As customer counts increase and sales teams expand, the informal processes that worked during startup become inadequate. Multiple team members need access to customer information, sales processes require standardization, and management needs visibility into performance metrics and revenue forecasts.
Team Collaboration Features become essential as businesses add sales team members and support staff. Shared customer records, communication histories, and task management ensure everyone has context for customer interactions regardless of who initiated previous communications.
Workflow standardization helps maintain service quality as teams grow and new members join. Automated reminders, approval processes, and follow-up sequences ensure consistent execution even when founders aren't personally involved in every customer interaction.
Reporting and analytics capabilities provide the visibility that growing businesses need to make informed decisions about resource allocation, market opportunities, and operational improvements. Understanding which marketing channels generate the best customers and which sales activities correlate with successful outcomes becomes crucial for efficient growth.
Integration Requirements expand as growing businesses add specialized tools for marketing, customer service, accounting, and operations. The CRM should serve as the central customer data hub that connects with other business applications rather than operating in isolation.
Scale-Up Complexity Management
Scale-up businesses face dramatically increased complexity as they expand into new markets, add product lines, or pursue different customer segments. CRM systems must accommodate multiple sales processes, diverse customer types, and sophisticated analytical requirements.
Multi-Pipeline Management enables businesses to track different sales processes for different customer segments or product lines. Enterprise sales follow different patterns than small business acquisitions, and the CRM should accommodate these variations without creating confusion or inefficiency.
Advanced automation becomes essential for managing larger volumes of leads and customers without proportional increases in team size. Intelligent lead routing, automated nurturing sequences, and sophisticated follow-up workflows enable small teams to handle enterprise-level customer volumes.
Customization capabilities allow scale-up businesses to adapt their CRM to specific industry requirements or unique business processes. Custom fields, specialized reports, and industry-specific integrations ensure the CRM supports business needs rather than forcing process changes to accommodate system limitations.
Performance Management features help scale-up businesses optimize team performance and identify improvement opportunities. Individual and team metrics, goal tracking, and performance analysis enable data-driven management decisions that drive continued growth.
Technology Architecture Considerations
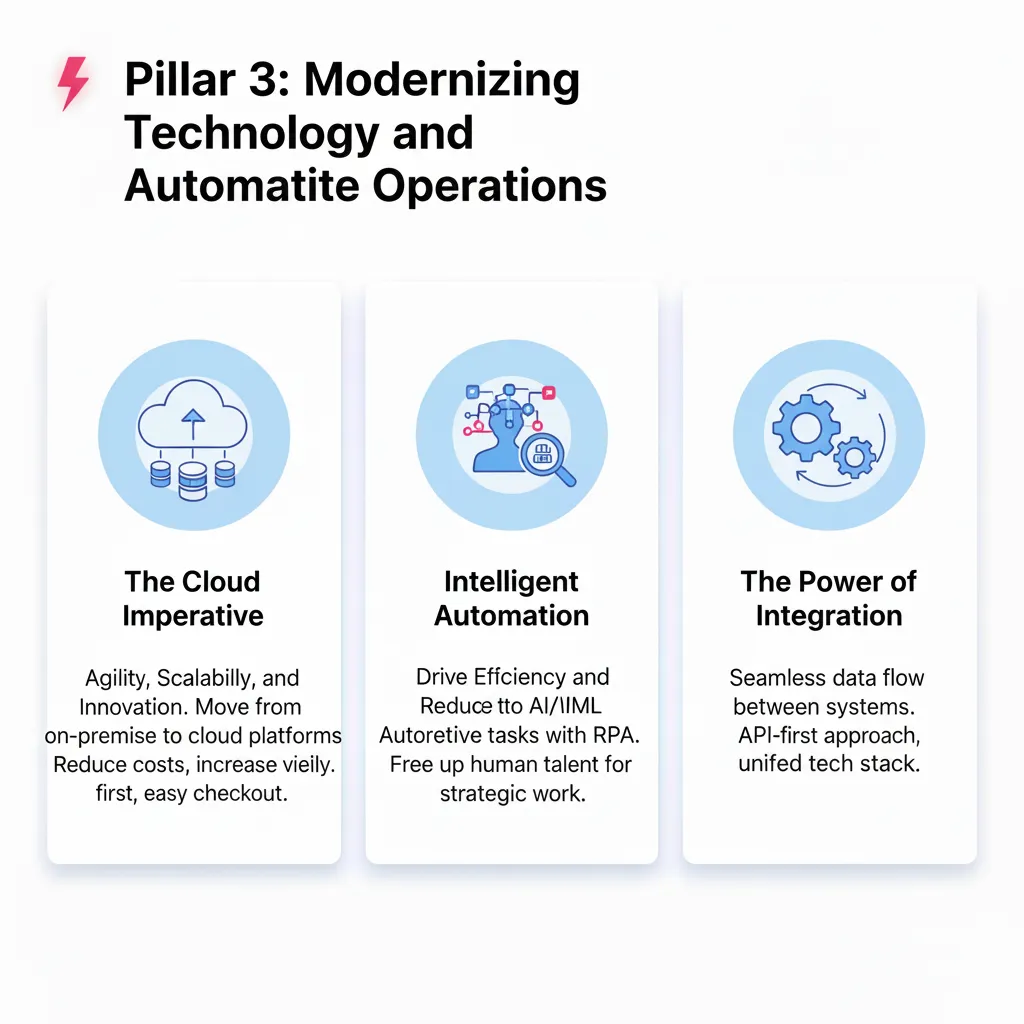
Scalable CRM architecture becomes crucial as businesses grow and their technology needs become more sophisticated. Cloud-based platforms offer advantages in scalability, integration capability, and ongoing maintenance that become increasingly important as businesses expand.
API-First Design ensures that the CRM can integrate with current and future business applications without requiring custom development or expensive consulting services. As businesses grow, they inevitably add specialized tools, and the CRM should accommodate these additions seamlessly.
Data management capabilities must scale to handle increasing volumes of customer information while maintaining performance and accessibility. Advanced search capabilities, data archiving, and backup systems become essential as customer databases grow larger and more valuable.
Security and compliance requirements often become more stringent as businesses grow and serve larger customers or enter regulated industries. The CRM platform should provide enterprise-level security features and compliance capabilities that can be activated as requirements evolve.
Mobile and Remote Access becomes increasingly important as teams grow and become more distributed. Field sales teams, remote employees, and executives traveling need full CRM access regardless of location or device.
Change Management Through Growth Phases
CRM evolution requires careful change management to ensure team adoption and minimize disruption during critical growth periods. Training programs should evolve along with CRM capabilities, ensuring team members can leverage new features effectively as they become available.
Gradual Feature Adoption prevents overwhelming teams with complexity while ensuring they benefit from CRM capabilities that support their current needs. Introduce advanced features systematically as teams become comfortable with foundational capabilities and business needs justify additional sophistication.
Data migration strategies become crucial when businesses outgrow their initial CRM selection. Plan for data export and import capabilities from the beginning to ensure smooth transitions if platform changes become necessary.
User feedback and adoption monitoring help identify which CRM features provide value and which create unnecessary complexity. Regular assessment ensures the CRM continues supporting business objectives rather than becoming an obstacle to efficiency.
ROI Optimization Across Growth Stages
CRM return on investment should improve as businesses grow and leverage more sophisticated capabilities. Track metrics like customer acquisition cost, sales cycle length, team productivity, and customer satisfaction to quantify CRM impact at different growth stages.
Feature Utilization Analysis reveals which CRM capabilities provide the highest value and which might be underutilized. This analysis helps optimize system configuration and identify training opportunities that could improve overall effectiveness.
Cost-benefit analysis should consider both direct CRM costs and the business impact of improved customer management capabilities. The ability to handle larger customer volumes without proportional team increases often justifies CRM investments that might seem expensive based on direct costs alone.
Future-Proofing CRM Strategy
Successful businesses plan their CRM strategy for multiple growth scenarios rather than just current needs. Consider how customer types might evolve, what additional markets you might enter, and how your sales processes might need to adapt as competitive landscapes change.
Scalability Testing evaluates how well your current CRM platform would handle 10x growth in customers, team size, or transaction volume. Understanding these limitations helps plan for infrastructure improvements before they become critical business constraints.
Technology roadmap alignment ensures your CRM strategy supports long-term business objectives rather than just immediate operational needs. Regular evaluation of platform capabilities and vendor direction helps identify when changes might be beneficial rather than waiting until current systems become inadequate.
The most successful scaling businesses view CRM as a strategic platform that evolves with their growth rather than a static tool that serves fixed requirements. They invest in platforms and partnerships that support long-term expansion while providing immediate operational benefits that justify ongoing investment and optimization efforts.